I am simply1 human being on earth wishing for a better life for all mankind through out the world. My wish..."PLEASE HELP THE WORLD FIND PEACE BY ENDING WARS, SERVING MANKIND, FIXING EARTH AND SAVING ... View MoreI am simply1 human being on earth wishing for a better life for all mankind through out the world. My wish..."PLEASE HELP THE WORLD FIND PEACE BY ENDING WARS, SERVING MANKIND, FIXING EARTH AND SAVING CHILDREN." ON THIS CHRISTMAS... AS I DO EVERDAY...I PRAY TO A HIGHER BEING FOR FORGIVENESS AND GUIDANCE FOR ALL.
War doesn't form a part of the world economy, but rather imposes massive destruction with the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP) estimating the economic impact of violence at over $19 trillion in 2023, or about 13.5% of global GDP, through destruction, lost productivity, displaced populations, and inflated defense spending. While some industries like military contractors see profit, the overall effect is destructive, diverting resources from productive growth into replacement and security, making peace economically more valuable.
Key Economic Impacts
Military expenditure, reconstruction, and humanitarian aid.
Indirect Costs Lost human capital (deaths, injuries, refugees), reduced investment, supply chain disruptions, and higher inflation.
Productivity Lost War destroys infrastructure and cripples industries, leading to significant GDP contraction in affected areas, sometimes by over 30%.
Resource Drain: Billions are spent on defense and conflict, resources that could otherwise foster innovation, development, and public welfare, notes the World Economic Forum and Brown University's Costs of War project.
War's "Economic Activity" vs. Growth
Replacement, not Growth Activity like rebuilding or arms manufacturing might show up as GDP, but it's merely replacing destroyed capital or meeting security needs, not creating new wealth.
Stimulus : While some argue war can stimulate economies (like WWII for the US), it's usually at the cost of massive debt and diversion from truly productive sectors, as highlighted in discussions on Reddit.
The True Value of Peace
Studies suggest global GDP would have been significantly higher (around 12% more) without violent conflict since 1970, proving peace is a massive economic benefit, according to the War Prevention Initiative.
Just by looking at the expenditure efforts and money in the world over war, conflict, and drugs the world would be more peaceful and more profitable if our nations chose to end wars, conflict, and drugs.
An end to war, conflict, and illegal drugs would likely redirect vast amounts of resources (financial, human, and intellectual) toward productive endeavors, potentially resulting in numerous significant advancements and improvements in the human condition.
Key areas of potential progress might include:
Scientific and Technological Breakthroughs Global cooperation and the redirection of resources from military budgets could accelerate research in areas like fusion energy, space exploration, medicine, and climate change solutions. Collaborative international efforts could lead to cures for diseases, sustainable technologies, and a deeper understanding of the universe.
Global Economic The immense financial burden of wars and the illicit drug trade (estimated at trillions of dollars annually in costs related to conflict, enforcement, healthcare, and loss of productivity) could be reallocated. This funding could support infrastructure development, education, and poverty reduction programs, potentially closing the gap between developed and developing nations and raising the global standard of living.
Improved Public Health and well being The cessation of violence would eliminate the direct casualties of war and significantly reduce the health and social crises linked to drug abuse. Resources currently used for emergency relief and rehabilitation could be invested in preventative healthcare, mental health services, and robust public health systems.
Social Cohesion and Trust A global environment free from major conflicts could foster greater trust between nations and within communities. This might lead to more stable governments, stronger social contracts, and a reduction in the fear and division that often accompany violence and criminal activity.
Environmental Restoration With increased cooperation and reduced focus on conflict, nations could work in concert to tackle pressing environmental issues like climate change, deforestation, and ocean pollution. Stable societies are often better equipped to invest in long-term environmental stewardship.
Ultimately, such a world could unlock humanity's full potential, creating a global civilization focused on innovation, cooperation, and the pursuit of a higher quality of life for all its inhabitants.
I am simply1 human being on earth wishing for a better life for all mankind through out the world. My wish..."PLEASE HELP THE WORLD FIND PEACE BY ENDING WARS, SERVING MANKIND, FIXING EARTH AND SAVING ... View MoreI am simply1 human being on earth wishing for a better life for all mankind through out the world. My wish..."PLEASE HELP THE WORLD FIND PEACE BY ENDING WARS, SERVING MANKIND, FIXING EARTH AND SAVING CHILDREN." ON THIS CHRISTMAS... AS I DO EVERDAY...I PRAY TO A HIGHER BEING FOR FORGIVENESS AND GUIDANCE FOR ALL.
War doesn't form a part of the world economy, but rather imposes massive destruction with the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP) estimating the economic impact of violence at over $19 trillion in 2023, or about 13.5% of global GDP, through destruction, lost productivity, displaced populations, and inflated defense spending. While some industries like military contractors see profit, the overall effect is destructive, diverting resources from productive growth into replacement and security, making peace economically more valuable.
Key Economic Impacts
Military expenditure, reconstruction, and humanitarian aid.
Indirect Costs Lost human capital (deaths, injuries, refugees), reduced investment, supply chain disruptions, and higher inflation.
Productivity Lost War destroys infrastructure and cripples industries, leading to significant GDP contraction in affected areas, sometimes by over 30%.
Resource Drain: Billions are spent on defense and conflict, resources that could otherwise foster innovation, development, and public welfare, notes the World Economic Forum and Brown University's Costs of War project.
War's "Economic Activity" vs. Growth
Replacement, not Growth Activity like rebuilding or arms manufacturing might show up as GDP, but it's merely replacing destroyed capital or meeting security needs, not creating new wealth.
Stimulus : While some argue war can stimulate economies (like WWII for the US), it's usually at the cost of massive debt and diversion from truly productive sectors, as highlighted in discussions on Reddit.
The True Value of Peace
Studies suggest global GDP would have been significantly higher (around 12% more) without violent conflict since 1970, proving peace is a massive economic benefit, according to the War Prevention Initiative.
Just by looking at the expenditure efforts and money in the world over war, conflict, and drugs the world would be more peaceful and more profitable if our nations chose to end wars, conflict, and drugs.
An end to war, conflict, and illegal drugs would likely redirect vast amounts of resources (financial, human, and intellectual) toward productive endeavors, potentially resulting in numerous significant advancements and improvements in the human condition.
Key areas of potential progress might include:
Scientific and Technological Breakthroughs Global cooperation and the redirection of resources from military budgets could accelerate research in areas like fusion energy, space exploration, medicine, and climate change solutions. Collaborative international efforts could lead to cures for diseases, sustainable technologies, and a deeper understanding of the universe.
Global Economic The immense financial burden of wars and the illicit drug trade (estimated at trillions of dollars annually in costs related to conflict, enforcement, healthcare, and loss of productivity) could be reallocated. This funding could support infrastructure development, education, and poverty reduction programs, potentially closing the gap between developed and developing nations and raising the global standard of living.
Improved Public Health and well being The cessation of violence would eliminate the direct casualties of war and significantly reduce the health and social crises linked to drug abuse. Resources currently used for emergency relief and rehabilitation could be invested in preventative healthcare, mental health services, and robust public health systems.
Social Cohesion and Trust A global environment free from major conflicts could foster greater trust between nations and within communities. This might lead to more stable governments, stronger social contracts, and a reduction in the fear and division that often accompany violence and criminal activity.
Environmental Restoration With increased cooperation and reduced focus on conflict, nations could work in concert to tackle pressing environmental issues like climate change, deforestation, and ocean pollution. Stable societies are often better equipped to invest in long-term environmental stewardship.
Ultimately, such a world could unlock humanity's full potential, creating a global civilization focused on innovation, cooperation, and the pursuit of a higher quality of life for all its inhabitants.
ANY PRESIDENT TRYING TO STOP RELIGIOUS PERSECUTION IN THE WORLD...IS A NEEDED REPRESENTATIVE FOR PEACE. STOPPIING WARS, SERVING MANKIND, SAVING CHILDREN. AND STANDING FOR PEACE SHOULD BE WHAT A PRESID... View MoreANY PRESIDENT TRYING TO STOP RELIGIOUS PERSECUTION IN THE WORLD...IS A NEEDED REPRESENTATIVE FOR PEACE. STOPPIING WARS, SERVING MANKIND, SAVING CHILDREN. AND STANDING FOR PEACE SHOULD BE WHAT A PRESIDENT STANDS FOR. TOO MANY TIMES WORLD LEADERS CHOOSE TO DEFY MORALITY FOR POPULARITY. IT IS REFRESHING TO SEE A LEADER TAKING ACTIONS THAT SAVE LIVES.
Nigeria is currently considered one of the most dangerous places in the world to be a Christian, with thousands of Christians killed annually by various extremist groups. The violence is attributed to several factors, including religious extremism, resource conflicts, and alleged government inaction or complicity.
Key Statistics and Perpetrators
Death Tolls: Watchdog groups report staggering figures. The Nigeria-based human-rights NGO, the International Society for Civil Liberties and the Rule of Law (Intersociety), reported over 7,000 Christians were killed in the first 220 days of 2025 alone, an average of 32-35 per day. Since 2009, over 50,000 Christians have been reportedly killed.
Perpetrators: The violence is mainly carried out by Islamist extremist groups, including Boko Haram, the Islamic State West Africa Province (ISWAP), and radicalized Fulani militants. These groups have targeted Christian communities, particularly in the northern and Middle Belt regions of Nigeria.
Global Impact: According to Open Doors, a Christian persecution watchdog group, more Christians are killed for their faith in Nigeria than in the rest of the world combined. In the reporting period for the 2025 World Watch List, 69% of all Christians killed worldwide were in Nigeria.
Nature of the Violence
The violence includes:
Targeted Killings: Christians are often targeted specifically because of their faith.
Village Raids: Armed groups attack and burn predominantly Christian farming communities, leading to mass displacement and a humanitarian crisis.
Abductions: Thousands of Christians, including clergy and students, have been kidnapped.
Destruction of Property: Churches and Christian-owned properties are frequently attacked and destroyed.
Government Response and International Concern
The Nigerian government has faced accusations of being unwilling or unable to address the violence, with some reports even suggesting government complicity or a lack of effective response from security forces. The government has refuted claims of a religious genocide, describing the situation as complex ethnic or resource-based clashes.
The situation has prompted international reactions:
Several U.S. lawmakers have urged the Biden administration (and more recently, the Trump administration in late 2025) to redesignate Nigeria as a "Country of Particular Concern" (CPC) for severe violations of religious freedom, a designation that can trigger sanctions.
The European Parliament has also condemned the massacres and called for measures to protect vulnerable Christian communities.
TRUMP WANTS WORLD PEACE.
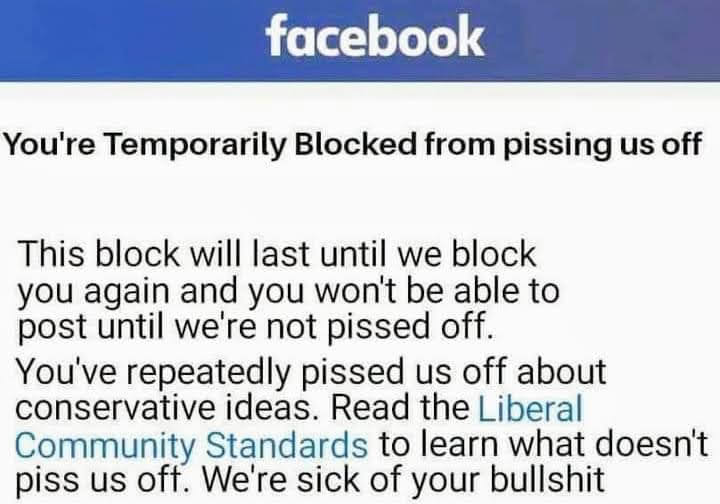
WELL AFTER HOWEVER LONG FACEBOOK HAS EXISTED...THEY FINALLY SUSPENDED AND DELETED MY ACCOUNT...THEY COULD NOT STOP TRUTH EXCEPT BY DENYING CONSTITUTIONAL FREEDOMS AND JUST USED SOCIALIST CRAP. HAS ANY... View MoreWELL AFTER HOWEVER LONG FACEBOOK HAS EXISTED...THEY FINALLY SUSPENDED AND DELETED MY ACCOUNT...THEY COULD NOT STOP TRUTH EXCEPT BY DENYING CONSTITUTIONAL FREEDOMS AND JUST USED SOCIALIST CRAP. HAS ANYONE ELSE GOT THIS MESSAGE? I GUESS I AM GOING TO HAVE TO PLAY DIRTY! CREATING FUTURE ACCOUNTS WITH MY 3 OTHER PHONES!
I POSTED YEARS AGO...THAT OBAMA, HILLARY, COMEY, BOLTON, SCHIFF, PELOSI, JAMES, AND OTHERS WILL BE PROSECUTED OVER HANDLING OF NATIONAL SECURITY INFORMATION HANDLING PROBLEMS. WHEN A FORMER PRESIDENT ... View MoreI POSTED YEARS AGO...THAT OBAMA, HILLARY, COMEY, BOLTON, SCHIFF, PELOSI, JAMES, AND OTHERS WILL BE PROSECUTED OVER HANDLING OF NATIONAL SECURITY INFORMATION HANDLING PROBLEMS. WHEN A FORMER PRESIDENT CAN BE PROSECUTED OVER POLITICAL SPECULATIONS... THEN EVERYONE CAN BE PROSECUTED FOR HANDLING OF CLASSIFIEN NATIONAL CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION.
IT IS BECOMING FACT THIS VERY DAY...AN I SEE MORE PROSECUTIONS ON THE WAY...BECAUSE THE TRUMP ADMINISTRATION IS SEARCHING CONGRESSIONAL DAILY RECORDS DOCUMENTATION FOR ABUSES BY FORMER ADMINISTRATIONS. WHETHER CONSERVATIVE OR LIBERAL EVERYONE WILL BE RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY ILLEGAL ACTIONS.
AS FACTS COME OUT AND VOTERS ACTUALLY SEE THE CRIMINAL POLITICAL ACTS COMMITTED... THE MORE VOTERS WILL BE TAKING ACTION
TO REMOVE PROBLEM POLITICIANS IN CONGRESS. I HOPE THERE IS A CLEANING OF CONGRESS. WE JUST NEED MORE HONEST AND MORAL PEOPLE SERVING THE PUBLIC. OUR PUBLIC SERVANTS SHOULD SIMPLY REFLECT THE WILL OF VOTERS. NOT FIGHT OUR DESIRES FOR THEIR OWN BIASED POLITICAL AGENDAS.
STOP SUPPORTING SOCIALIST IGNORANCE...
page=1&profile_user_id=25176&year=&month=
Load More